SSD Form Factor Trends: M.2 SSD vs. EDSFF Hot-Swap
How Should Enterprises Choose SSD Form Factors?
As digital transformation accelerates and data storage demands surge, SSDs have become essential for enterprise data centers. But between the widely adopted M.2 and the emerging Enterprise and Datacenter Standard Form Factor (EDSFF), how do businesses determine the best fit for their specific needs? Here's a concise overview:
M.2 SSD:

Key Features:
-
Form Factors: Available in M.2 2230、M.2 2242、M.2 2280、M.2 22110 to accommodate diverse applications.
-
Compatibility: Ideal for space-constrained devices such as notebooks, edge computing solutions, embedded systems, and industrial controls.
-
Low Power Consumption: Reduces electricity costs, supports energy-efficient initiatives, and prolongs device lifespan.
Applications:
- Consumer: Gaming and content creation, requiring fast loading speeds and smooth 4K editing.
- Industrial: Automation, medical devices, and transportation systems demanding compact and robust storage solutions.
- Edge Computing: Embedded systems requiring high performance and low energy usage.
CL6 M.2 2280
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen4 x4
Sequential Read: 6,000 MB/s
Sequential Write: 5,300 MB/s
EDSFF: High Performance, Hot-Swap Capability—New Enterprise Standard

Key Features:
-
Form Factors: Includes E1.S, E1.L, E3.S, and E3.L, optimized for AI, high-performance computing (HPC), and database applications.
-
High Storage Density: E1 SSDs maximize storage capacity in 1U chassis, meeting large-scale data processing requirements.
-
Hot-Swap Functionality: Enables SSD replacement without downtime, significantly reducing maintenance costs and operational risks.
-
Superior Thermal Management: Excellent cooling efficiency ensures stable, long-term data center operation.
-
Enhanced Performance: Supports up to 70W power budget for top-tier SSD performance.
Applications:
-
Data Centers: Cloud computing and HPC environments needing high-density storage and consistent performance.
-
Enterprise Servers: AI/ML processing, virtualization, and real-time analytics demanding high IOPS and low latency.
-
Edge Servers: Automotive data logging, defense, and aerospace applications requiring capacity, durability, and hot-swap flexibility.
PJ1 E1.S (5.9/9.5mm)
NAND Flash: 3D TLC NAND Flash
Interface: PCIe® Gen4 x4
Sequential Read: UP to 6600 MB/s
Sequential Write: UP to 3500 MB/s
Enterprise SSD Market Trend:EDSFF (E1.S / E3) is Becoming Mainstream
According to Forward Insights' 2022–2029 shipment forecast for enterprise PCIe SSDs:
-
EDSFF SSD:
-E1.S: Accounted for only 7% in 2022, projected to rise to around 30% by 2029.
Strong demand driven by cloud and AI servers that require high density and hot-swappable solutions.
-E3: Starting from 0% in 2022 and expected to exceed 35% by 2029.Indicates rapid adoption by high-power, high-capacity servers and data centers.
-
M.2 SSD:
Still essential for industrial control systems, edge servers, and lightweight server applications that require low power consumption and compact form factors.
However, market share is projected to decline from 30% in 2022 to about 23% by 2029.
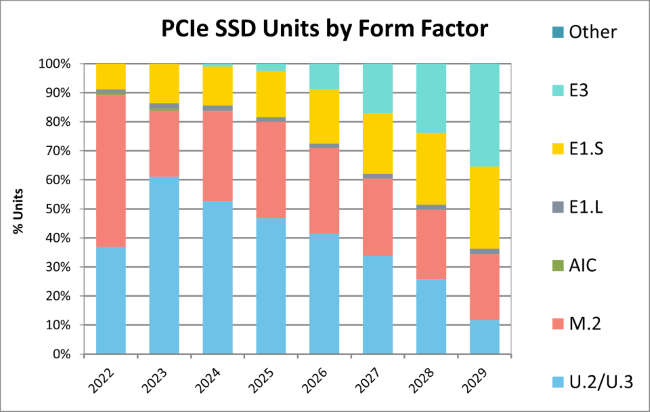
Choosing the Right SSD Form Factor:
-
Space & System Design: Is storage space limited, or is there sufficient room for hot-swap drives to improve maintenance efficiency?
-
Performance & Cooling Needs: Does the system require sustained high performance and effective heat dissipation under heavy loads?
-
Maintenance & Scalability: Will frequent SSD replacements or expansions be needed to keep pace with rapid business growth?
| Specification | M.2 SSD | EDSFF SSD |
| Form Factors | E1.S、E1.L、E3.S、E3.L | |
| Power |
Typical range 2-12W (interface dependent) |
High performance, typical 10-25W, up to 70W (E3.L) |
| Thermal |
Limited (depends on system design) |
Advanced cooling, optimized for data centers |
| Hot-Swap | Not supported | Supported |
Conclusion: Stay Ahead with the Latest SSD Trends
Choosing the right SSD impacts not only performance and data access efficiency but also operational cost and manageability. Compact M.2 SSDs suit embedded and edge applications, whereas EDSFF SSDs—featuring higher power handling, hot-swapping, and enhanced cooling—are ideal for demanding, high-density data centers and AI-driven workloads.
SSSTC provides comprehensive enterprise and industrial SSD solutions designed for exceptional performance and reliability. Contact SSSTC's expert team today for tailored enterprise SSD recommendations!


__24C05D67dI.webp)


__24C15hqqtC.png)
__24C15wOdCC.png)









__24C05XQ2my.jpg)






__24C05fplcZ.png)
__24C05vgHYC.png)


